Digitaria patens
|
|
|
|
Family: Poaceae
Texas Cottontop
[Trichachne patens Swallen] |
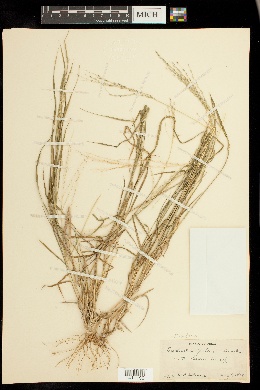
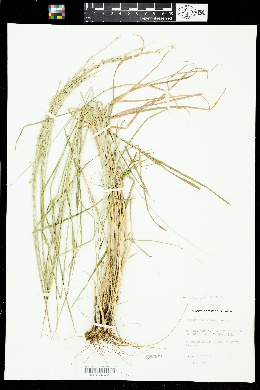
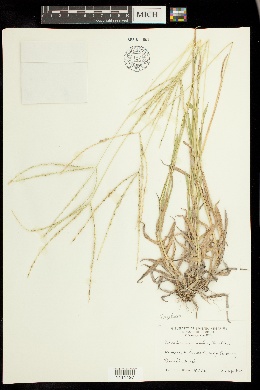
Plants perennial; cespitose, neither rhizomatous nor stoloniferous. Culms 40-90 cm, erect, sometimes geniculate, not rooting, at the lower nodes. Leaves mainly cauline; basal sheaths villous; upper sheaths glabrous or sparsely to densely hirsute, hairs papillose-based; ligules (1)1.5-4 mm, entire to lacerate; blades 5-15 cm long, 1-4 mm wide, glabrous or sparsely pubescent. Panicles with 4-10 spikelike primary branches on (4)10-18 cm rachises; primary branches 4-10 cm, usually divergent at maturity, varying to ascending, axes not wing-margined, with spikelets in unequally pedicellate pairs; internodes (4.5)6-15 mm (mid branch); secondary branches rarely present; shorter pedicels 2-2.5 mm; longer pedicels 7-8 mm; terminal pedicels of primary branches 7.4-20 mm. Spikelets homomorphic, 3.7-5.8 mm (including pubescence), 2.9-4.3 mm (excluding pubescence). Lower glumes 0.3-0.5 mm; upper glumes 2.4-3.5 mm (excluding pubescence), 3-veined, densely villous, hairs 1.5-4 mm, silvery-white to purple, spreading at maturity; lower lemmas 2.8-4.2 mm (excluding pubescence), exceeding the upper lemmas by 0.8-2.2 mm, 5-veined and the veins equally spaced or 7-veined and the lateral veins closer to each other than to the central vein, margins densely villous, hairs 1.5-4 mm, silvery-white to purple, spreading at maturity, apices acuminate; upper lemmas 2.6-3.2 mm, lanceolate, brown when immature, dark brown at maturity, acuminate. 2n = 72. Digitaria patens is endemic to southwestern and southern Texas and adjacent Mexico. It grows in well-drained, usually sandy soils, often in disturbed habitats. Gould (1975) suggested that it might be an octoploid derivative of D. californica. Perennials, Terrestrial, not aquatic, Rhizomes present, Rhizome short and compact, stems close, Stems nodes swollen or brittle, Stems erect or ascending, Stems caespitose, tufted, or clustered, Stems terete, round in cross section, or polygonal, Stem internodes hollow, Stems with inflorescence less than 1 m tall, Stems, culms, or scapes exceeding basal leaves, Leaves mostly cauline, Leaves conspicuously 2-ranked, distichous, Leaves sheathing at base, Leaf sheath mostly open, or loose, Leaf sheath hairy, hispid or prickly, Leaf sheath and blade differentiated, Leaf blades linear, Leaf blades very narrow or filiform, less than 2 mm wide, Leaf blades 2-10 mm wide, Leaf blades mostly flat, Leaf blades mostly glabrous, Ligule present, Ligule an unfringed eciliate membrane, Inflorescence terminal, Inflorescence solitary, with 1 spike, fascicle, glomerule, head, or cluster per stem or culm, Inflorescence a panicle with digitately arranged spicate branches, Infl orescence with 2-10 branches, Inflorescence branches 1-sided, Lower panicle branches whorled, Rachis angular, Flowers bisexual, Flowers unisexual, Spikelets pedicellate, Spikelets dorsally compressed or terete, Spikelet less than 3 mm wide, Spikelets with 1 fertile floret, Spikelets with 2 florets, Spikelet with 1 fertile floret and 1-2 sterile florets, Spikelets paired at rachis nodes, Spikelets all alike and fertille, Spikelets bisexual, Spikelets disarticulating below the glumes, Spikelets secund, in rows on one side of rachis, Rachilla or pedicel glabrous, Glumes present, empty bracts, Glumes 1 clearly present, the other greatly reduced or absent, Glumes 2 clearly present, Glumes distinctly unequal, Glumes equal to or longer than adjacent lemma, Glume equal to or longer than spikelet, Glume surface hairy, villous or pilose, Glumes 4-7 nerved, Lemmas thin, chartaceous, hyaline, cartilaginous, or membranous, Lemma similar in texture to glumes, Lemma 5-7 nerved, Lemma apex acute or acuminate, Lemma awnless, Lemma margins thin, lying flat, Lemma straight, Palea present, well developed, Palea membranous, hyaline, Palea about equal to lemma, Stamens 3, Styles 2-fid, deeply 2-branched, Stigmas 2, Fruit - caryopsis, Caryopsis ellipsoid, longitudinally grooved, hilum long-linear.
|