|
|
|
|
Family: Amaranthaceae
Siberian Bugseed
[Corispermum hyssopifolium f. simplex F. Zimm. ex Hegi, moreCorispermum hyssopifolium var. membranaceum Bisch. ex Graebn.] |
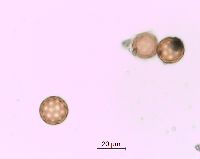
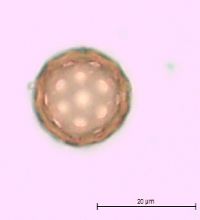
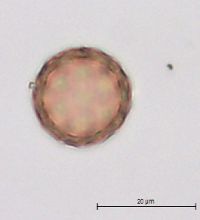
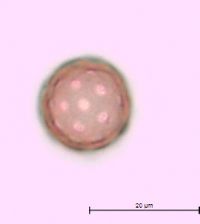
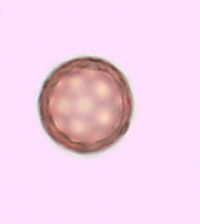
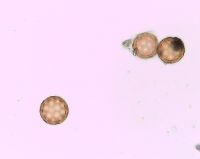
Plants branched from base or nearly so, 10-45(-60) cm, sparsely covered with dendroid or almost stellate hairs, becoming glabrous. Leaf blades linear-lanceolate, linear, or occasionally narrowly linear, usually plane, 1.5-4 × (0.1-)0.2-0.4(-0.5) cm. Inflorescences usually compact and dense, rarely ± lax and interrupted in proximal 1/2, clavate, narrowly clavate, or almost ovate in outline. Bracts ovate or ovate-lanceolate (rarely narrowly ovate-lanceolate), ca. (0.5-)1-3 × 0.4-0.8 cm. Perianth segment 1. Fruits light brown, brown, dark brown, or deep olive green, often with reddish brown spots and whitish warts, convex abaxially, usually plane or slightly concave adaxially, obovate or obovate-elliptic, usually broadest beyond middle, (3.2-)3.5-4.5(-4.7) × (2-)2.4-3 mm; wing translucent only at margin (or in marginal 1/2), thick, 0.2-0.4(-0.5) mm wide, margins entire or indistinctly erose, apex broadly triangular, rarely rounded or very indistinctly emarginate. Flowering late summer-fall. Sand dunes, sandy and gravely shores, waste places; 0-100 m; Alta., Man., Ont., Que., Sask.; Ill., Ind., Mich., Minn., N.Y., N.Dak., Ohio, Wis.; introduced in Europe; Asia (se Siberia). Corispermum pallasii is placed in subsect. Pallasiana Mosyakin, which is evidently of Asian origin. Related taxa are widespread in southern Siberia, central Asia, Mongolia, and China. It is also widespread in Europe, where it was most probably initially introduced in Germany by German botanists and gardeners, who obtained seeds from Siberia through Russian botanical gardens (G. F. Schnittspahn 1851; U.-V. Köck 1986). In Europe this species was known as C. leptopterum (Ascherson) Iljin. It is not known yet whether this species was introduced to North America or is at least partly native within its North American range. Judging from the very close taxonomic affinity of C. pallasii to other, native North American taxa (e.g., C. americanum, C. villosum, C. ochotense, C. hookeri) and morphological similarity of its fruits to some fossil Corispermum fruits, the hypothesis of the native status of C. pallasii in North America seems to be preferable; secondary introduction of some populations from Europe is also not improbable.
Annual herb 10 cm - 0.6 m tall Stem: upright or ascending, branched from at or near base, sparsely covered with branched (dendroid) or nearly star-shaped (stellate) hairs, often becoming hairless with age. Leaves: alternate, stalkless, 1.5 - 4 cm long, 1 - 5 mm wide, linear to narrowly lance-shaped with a flat base and pointed tip, usually flat. Inflorescence: a terminal, dense spike of flowers, narrowly club-shaped (clavate) to almost egg-shaped. Flowers: solitary in axils of leaf-like bracts, greenish, tiny, scale-like, with one sepal and no petals. Bracts 0.5 - 3 cm long, 4 - 8 mm wide, egg-shaped to egg- lance-shaped. Stamen one, exserted. Stigmas two. Fruit: an achene, vertical, stalkless, brownish to dark olive green, often spotted reddish brown, 3.5 - 4.5 mm long, 2 - 3 mm wide, reverse egg-shaped, usually broadest past the middle, convex beneath, more or less flat above, whitish-warty, winged. Wing translucent at margin, to 0.5 mm wide, thick. Similar species: No information at this time. Flowering: July to September Habitat and ecology: Introduced from Eurasia. Characteristically found on the sandy beaches of Lake Michigan. Occurence in the Chicago region: non-native Etymology: Corispermum comes from the Greek words coris, meaning bedbug, and sperma, meaning seed. Pallasii is named after Peter Simon Pallis, a German Botanist and Zoologist. Author: The Morton Arboretum From Flora of Indiana (1940) by Charles C. Deam On sand dunes; known from Lake, La Porte, and Porter Counties. ...... Indiana Coefficient of Conservatism: C = 3 Wetland Indicator Status: UPL Diagnostic Traits: leaves linear, to 4 mm wide; inflorescences densely spicate, narrowly clavate to ovate in outlines; flowers solitary in the axiles of acuminate bracts; larger fruits 2.3-3.3 mm wide, translucent-winged. |
This project was made possible in part by the Institute of Museum and Library Services [MG-70-19-0057-19].
Powered by Symbiota