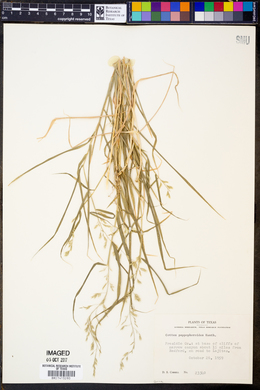
Cottea pappophoroides
|
|
|
|
Family: Poaceae
Cotta Grass
|
Culms 25-70 cm. Blades 5-15 cm long, 4-7 mm wide. Panicles 8-15 cm long, 2-6 cm wide, green or purplish; branches loosely ascending. Spikelets 5-10 mm (including the awns). Glumes 4-5 mm; lemmas 3-4 mm, conspicuously long-pilose basally, awns and teeth more or less alternating. Caryopses about 1.5 mm, plump, elliptical; embryos about 1/2 as long as the caryopses. 2n = 20. Cottea pappophoroides grows on open hillsides from Arizona and Texas south to central Mexico, and from Ecuador to Argentina. Dr. David Bogler, USDA NRCS PLANTS Database Perennials, Terrestrial, not aquatic, Stems nodes swollen or brittle, Stems erect or ascending, Stems caespitose, tufted, or clustered, Stems terete, round in cross section, or polygonal, Stem nodes bearded or hairy, Plants conspicuously hairy, grayish, or wooly, Stem internodes hollow, Stems with inflorescence less than 1 m tall, Stems, culms, or scapes exceeding basal leaves, Leaves mostly basal, below middle of stem, Leaves mostly cauline, Leaves conspicuously 2-ranked, distichous, Leaves sheathing at base, Leaf sheath mostly open, or loose, Leaf sheath hairy, hispid or prickly, Leaf sheath and blade differentiated, Leaf blades linear, Leaf blades 2-10 mm wide, Leaf blades mostly flat, Leaf blades more or less hairy, Ligule present, Ligule a fringe of hairs, Inflorescence terminal, Inflorescence a contracted panicle, narrowly paniculate, branches appressed or ascending, Inflorescence solitary, with 1 spike, fascicle, glomerule, head, or cluster per stem or culm, Inflorescence branches more than 10 to numerous, Peduncle or rachis scabrous or pubescent, often with long hairs, Flowers bisexual, Spikelets pedicellate, Spikelets laterally compressed, Spikelet 3-10 mm wide, Spikelets with 3-7 florets, Spikelets solitary at rachis nodes, Spikelets all alike and fertille, Spikelets bisexual, Spikelets disarticulating above the glumes, glumes persistent, Rachilla or pedicel hairy, Glumes present, empty bracts, Glumes 2 clearly present, Glumes equal or subequal, Glumes 8-15 nerved, Lemmas thin, chartaceous, hyaline, cartilaginous, or membranous, Le mma similar in texture to glumes, Lemma 8-15 nerved, Lemma body or surface hairy, Lemma apex dentate, 3-5 fid, Lemma teeth unequal. central tooth longer, Lemma with 7-15 awns, Lemma awn less than 1 cm long, Lemma awned from tip, Lemma awns straight or curved to base, Lemma margins thin, lying flat, Lemma straight, Callus or base of lemma evidently hairy, Callus hairs shorter than lemma, Callus hairs equal to lemma, Lemma surface pilose, setose or bristly, Palea present, well developed, Palea membranous, hyaline, Palea longer than lemma, Palea 2 nerved or 2 keeled, Palea keels winged, scabrous, or ciliate, Stamens 3, Styles 2-fid, deeply 2-branched, Stigmas 2, Fruit - caryopsis, Caryopsis ellipsoid, longitudinally grooved, hilum long-linear.
FNA 2003 Common Name: cotta grass Duration: Perennial Nativity: Native Lifeform: Graminoid General: Tufted perennial without rhizomes, stems 30-70 cm tall, ascending or erect from hard knotty bases; stems softly pilose below panicle, with bearded nodes. Vegetative: Sheaths longer than internodes, pilose, rounded on backs; blades 3-7 mm broad, flat or folded, pilose on both surfaces; ligule of hairs. Inflorescence: Narrow but open panicle with stout erect-spreading branches, 6-20 cm long, 2-6 cm wide; spikelets 7-10 mm long, with 6-10 florets, the upper florets reduced; disarticulating above glumes and between florets; self-fertilizing spikelets produced in axils of lower leaf sheaths; glumes subequal, 4-5 mm long, broadly lanceolate, with 7-13 fine but distinct nerves, the midnerve sometimes continuing as short awn; lowermost lemma as long as glumes, hairy near base, with nine to thirteen nerves; caryopsis oblong, about 1.5 mm long. Ecology: Rocky slopes, hillsides, and plains below 5,000 ft (1524 m); flowers late summer to fall. Distribution: s AZ, s NM, s TX; south through Mexico to Argentina. Notes: Cottea is a monotypic (one species in the genus) North American genus. Distinguished by being a cespitose perennial with hard, knotty bases; leaf sheaths with pilose hairs and stems with hairy nodes; panicles with hairy branches and spikelets of 6-10 florets that are conspicuously hairy, especially at the base and many awns. The many awns and hairs give the spikelets a fluffy appearance. Ethnobotany: Unknown Etymology: Cottea is named for J.G. Cotta von Cottendorf (1796-1863) a German patron of science; pappohphoroides comes from the Latin pappus, the tufts of hairs clustered around Asteraceae achenes (think of dandelion seeds), and Greek oeides, resembling or being like something. Synonyms: None Editor: SBuckley 2010, FSCoburn 2014, AHazelton 2015 |
|
|
|